Sprott’s 2026 outlook: metals, debt and tariffs – key signals for mine planners
Reviewed by Joe Ashwell
First reported on MINING.com
30 Second Briefing
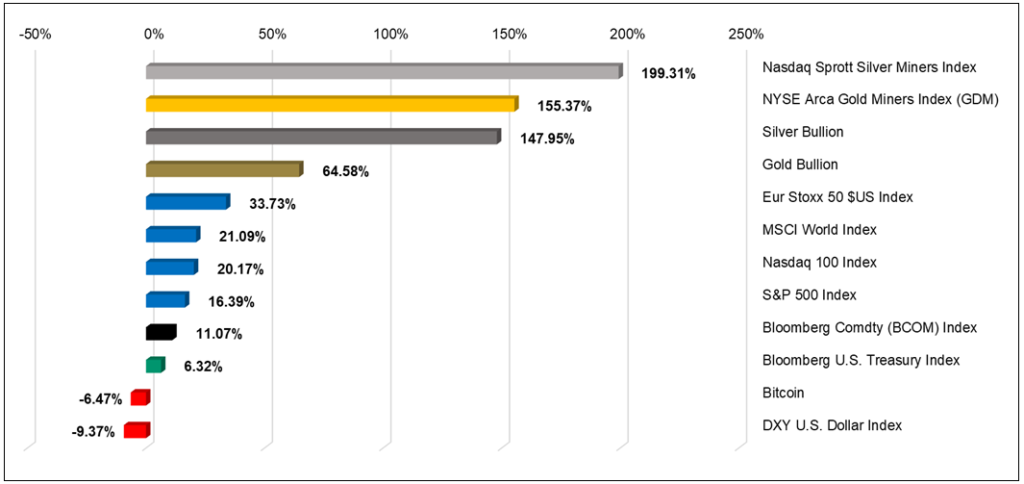
Deglobalisation, fractured metal inventories and the “debasement trade” into hard assets are expected by Sprott to drive 2026 markets, with US public debt above $38 trillion and copper in the US trading up to 30% higher than London prices in 2025 as tariffs and stockpiling distorted flows. Central banks, led by China, are projected to keep buying gold heavily after reserves freezes in 2022, while silver’s dual role as monetary hedge and critical input for clean energy and AI infrastructure supports its bull cycle. Uranium, copper and rare earths remain key watchpoints, with $80 billion in new US reactor support, 17‑year average copper mine lead times, and rare earth supply still dominated by China.
Technical Brief
- Sprott flags national stockpiling of rare earths, copper, PGMs and aluminium as a structural demand driver.
- Resource nationalism and export controls are explicitly cited as catalysts for further critical mineral supply bottlenecks.
- Sprott’s “debasement trade” thesis links chronic post‑pandemic fiscal deficits directly to sustained hard‑asset allocation.
- For project developers, fragmented inventories imply higher regional basis risk and greater emphasis on offtake and jurisdictional diversification.
Our Take
Sprott’s emphasis on uranium and critical minerals in 2026 lines up with our recent coverage of Meta’s 6.6 GW US nuclear power build-out and Sprott-linked uranium financing, signalling that AI‑driven data centre loads are becoming a material demand driver for uranium and associated rare earths rather than a side theme.
The 30% US copper price premium over London and the 17‑year average copper mine development time suggest North American copper projects in our database with existing permits or brownfield expansion potential are likely to attract disproportionate capital, as they can monetise regional tightness well before new greenfield supply arrives.
With US public debt at US$38 trillion and gold already flagged in our corpus as being in a bull cycle since 2022, Sprott’s 2026 outlook effectively reinforces a pattern in our coverage where gold and silver are being framed less as short‑term trades and more as structural hedges against fiscal and monetary strain.
Prepared by collating external sources, AI-assisted tools, and Geomechanics.io’s proprietary mining database, then reviewed for technical accuracy & edited by our geotechnical team.
Related Articles
Related Industries & Products
Mining
Geotechnical software solutions for mining operations including CMRR analysis, hydrogeological testing, and data management.
Construction
Quality control software for construction companies with material testing, batch tracking, and compliance management.
CMRR-io
Streamline coal mine roof stability assessments with our cloud-based CMRR software featuring automated calculations, multi-scenario analysis, and collaborative workflows.
HYDROGEO-io
Comprehensive hydrogeological testing platform for managing, analysing, and reporting on packer tests, lugeon values, and hydraulic conductivity assessments.
GEODB-io
Centralised geotechnical data management solution for storing, accessing, and analysing all your site investigation and material testing data.


