Rio Tinto–Glencore ASX coal spin-off: portfolio and risk takeaways for mine teams
Reviewed by Joe Ashwell
First reported on MINING.com
30 Second Briefing
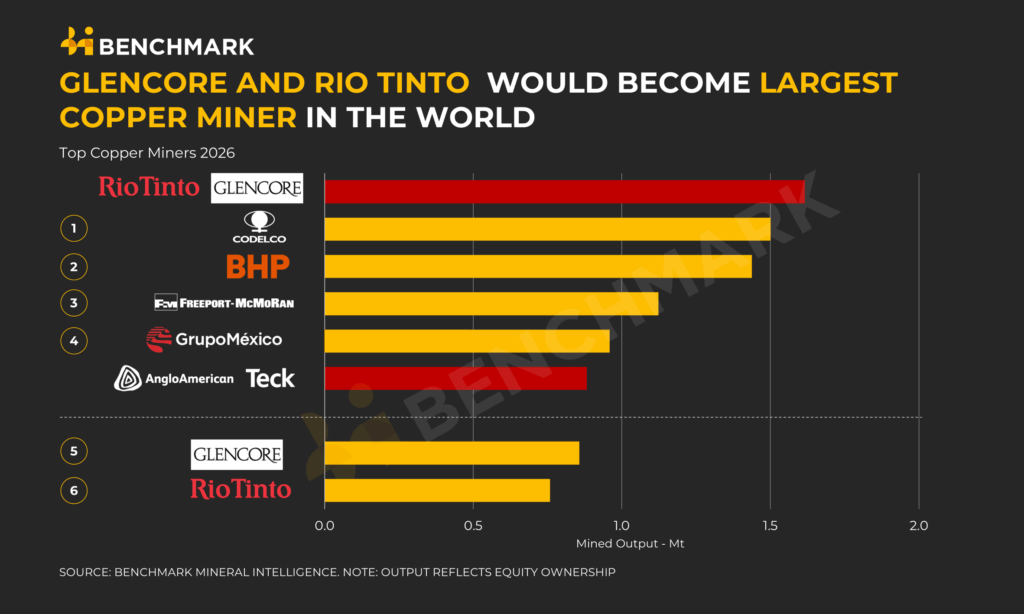
Rio Tinto and Glencore are weighing a spin-off of Glencore’s coal assets into a separate ASX-listed vehicle, similar to BHP’s South32 demerger, as part of early-stage merger talks that must yield a proposal by 5 February under UK takeover rules. Glencore’s coal operations in New South Wales, Queensland, central Africa and Latin America generate about 8% of a combined group’s US$45.6 billion EBITDA, while its trading arm contributes roughly 9% and remains structurally contentious. The merger would create the world’s largest miner and the leading copper producer at around 7% of global output, intensifying antitrust, coal-mandate and high-risk jurisdiction scrutiny.
Technical Brief
- Glencore currently runs 13 coal mines across New South Wales and Queensland, underpinning any ASX coal vehicle.
- Banking advisory teams are already mandated to structure valuation, premium and governance for the proposed combination.
- A coal carve‑out is explicitly benchmarked against BHP’s South32 demerger model from a decade earlier.
- Alternative structures under discussion include a pre‑merger Glencore coal spin‑off or a copper‑only acquisition by Rio.
- Copper spot prices above US$13,000/t materially strengthen the economic case for consolidating copper portfolios.
- S&P projects up to 10 Mt/a copper supply deficit by 2040, with demand potentially 50% higher.
Our Take
In our database of 628 Mining stories, Rio Tinto increasingly appears in copper and iron ore growth pieces (such as the Nuton copper offtake with Amazon Web Services and the Pilbara iron ore MoUs with BHP), so a coal spin-off would align its listed profile more tightly with those future-facing commodities rather than legacy thermal coal exposure in Australia.
Glencore’s 13 coal mines in New South Wales and Queensland currently contribute only 8% of combined group EBITDA, which suggests an ASX coal vehicle could be valued more on cash-yield and mine-life optionality than on group-level growth metrics that are increasingly driven by copper and trading earnings (9% of the total).
With S&P’s ‘Copper in the Age of AI’ projections in this piece pointing to a 50% rise in copper demand and a 10 Mt/y deficit by 2040, any Rio Tinto–Glencore portfolio reshaping away from coal strengthens their ability to argue for capital reallocation into copper, where the combined group already accounts for about 7% of global output in our coverage set.
Prepared by collating external sources, AI-assisted tools, and Geomechanics.io’s proprietary mining database, then reviewed for technical accuracy & edited by our geotechnical team.
Related Articles
Related Industries & Products
Mining
Geotechnical software solutions for mining operations including CMRR analysis, hydrogeological testing, and data management.
CMRR-io
Streamline coal mine roof stability assessments with our cloud-based CMRR software featuring automated calculations, multi-scenario analysis, and collaborative workflows.
HYDROGEO-io
Comprehensive hydrogeological testing platform for managing, analysing, and reporting on packer tests, lugeon values, and hydraulic conductivity assessments.
GEODB-io
Centralised geotechnical data management solution for storing, accessing, and analysing all your site investigation and material testing data.


